Dry Fertilizer Unit Calibration
Chuck Bornt, Team Leader, Extension Vegetable Specialist
Eastern New York Commercial Horticulture
The first sweet corn was planted under plastic and some under rowcovers last week which is a sure sign of spring right? If you didn't get it done over the winter, now is the time to finish getting equipment prepared for planting season - especially calibrating your dry fertilizer units. Over time, the augers, fertilizer disk openers and other parts can get worn out, changing the amount of fertilizer actually coming out.
Calibrating your fertilizer delivery rates through your planter is really not that difficult using a 1/50th of an acre calculation. Follow these steps:
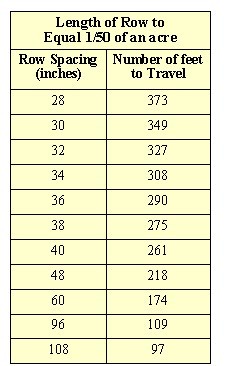
- Look at Table 1 to determine how far to drive to equal 1/50th of an acre using your row spacing. For example—if your between-row spacing is 30" then you need to travel 349 feet to equal 1/50th of an acre. If your row spacing doesn't show up in the table, figure it out by dividing 43,560 by your spacing in feet and multiply by 0.02 and that is the distance you need to travel. Use flags or stakes to mark the distance required.
- Disconnect the drop tubes from your fertilizer hoppers and attach a bag or bucket underneath to catch the fertilizer (be sure to weigh the bucket first in order to tare your scale or subtract it from the weight after you catch the fertilizer). Make sure the hoppers are at least half full of fertilizer when you start. Make sure augers are "primed" by dropping the planter and moving forward until you see fertilizer coming out of the hoppers.
- Remove the bucket or bag and weigh it separately and multiply by 50. The value you get should be the approximate amount of fertilizer you're applying in pounds per acre. Do not add the fertilizer amounts from the hopper together. The value you get per row should be similar. If they are not, you may need to exam your augers to see if they are worn differently etc. If the rates are similar, but not what you thought you were putting out, you need to review your manual and adjust your sprocket settings. I would also recommend you do this 2 or 3 times and average the values together per row. Repeat this process every time you change a sprocket combination as well.
- For example, if the amount you weigh from one tube equals 6 pounds, then you are applying 300 pounds of fertilizer per acre. You can also use the same formula and techniques to determine how much fertilizer you're using if you are sidedressing with a Cole or other type of unit.
Also be sure to check your fertilizer disk openers and make sure they are not worn out. Fertilizer injury is not caused only by high rates, but more often it's because the opener disks were worn or miss-aligned. For example, if your fertilizer openers are supposed to be 15" and you measure them at 13 ½", you're placing the fertilizer 1 ½" closer to the seed - the rule of thumb for fertilizer placement is 2" below the seed and 2" to the side of the seed - Anything closer than this can result in fertilizer burn. This is only one part of the planting operation! Be sure to check all the other parts of your planter including the meters, seed tubes etc. If you have questions, please feel free to call Chuck Bornt at 518‑859‑6213.

Upcoming Events
Wine Sensory Evaluation Workshop
April 26, 2024 : Wine Sensory Evaluation Workshop
Staatsburg, NY
In collaboration with Jeremy Schuster, Viticulture Specialist at the ENYCHP, Dr. Anna Katharine Mansfield and Chris Gerling, Enology Extension Specialists with the Cornell Craft Beverage Institute, will be presenting a wine production-focused, interactive workshop on sensory evaluation.












































